On the web, you can find a lot of controversy regarding the hacking of Bitcoin Wallets. The result of the discussion is the selection of two main ways: by gaining access to the PC of cryptocurrency owners and through the selection of private keys (с помощью личных данных пользователя).
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies traditionally attract increased attention хакеров of various calibers, who not only use them in their illegal activities, but also actively steal them not only from exchanges, but also from ordinary users.
With the help of advanced technology, hackers are finding new ways to steal funds, but the basic and time-tested methods remain the same, as new people enter the cryptocurrency space every day, who often do not have an adequate level of knowledge and awareness to counter such attacks.
Ниже перечислены основные уловки и трюки хакеров, зная о которых пользователи могут как минимум обезопасить свои монеты.
Getting access to the PC and to the server on this option, the fault lies entirely with the owner of the Bitcoins. He did not protect the computer himself and allowed hackers to steal personal data. For the second method, you need software to hack Bitcoin wallets.
Если приводить случаи из истории, за время существования Bitcoin произошло много резонансных событий:
- 2011 – Mt.Gox cryptocurrency exchange was hacked, resulting in the theft of 650,000 BTC.
- 2014 – theft of coins from the Cryptsy exchange. The attackers managed to steal 13,000 Bitcoins and another 300,000 Litecoins.
- 2015 – the Bitstamp exchange platform suffered, from which 19 thousand BTC were stolen. At that time it was about 5 million dollars.
- 2016. Between April and August, three exchanges suffered at once – ShapeShift, Gatecoin and Bitfinex. In the first case, about 315 Bitcoins were stolen, in the second – 250, and in the third – 119756 BTC.
- 2017 – 4700 BTC stolen from NiceHash. 2018 – theft of 158.89 BTC from a Ukrainian. True, the abduction was not networked, but physical. The owner was locked in the garage and threatened to give away everything he had.
- 2019 – On May 7, the Binance exchange was hacked and lost about 7,000 bitcoins.
- 2020 — Altsbit exchange hack. The hackers managed to gain access to the trading platform’s hot wallets overnight.
These are far from all cases related to the hacking of cryptocurrency exchanges and online wallet services. At the end of 2021, there was information in the news about the arrest of a programmer from China, who stole BTC in the amount of $3 million. The attacker was a moderator of a group about hacking cryptocurrency exchangers, published news about methods of theft, ways to protect against fraud. One of the users was added to the group and, while reading the next news, downloaded an application that creates a new address for the Bitcoin wallet. As a result, all the coins from the account were stolen. The hackers managed to carry out three thefts worth about $3 million.
Most of the cases of hacking involve cryptocurrency exchanges, but this does not mean that Bitcoin itself is “weak”. The cryptocurrency network is not responsible for the irresponsible storage of Bitcoin addresses. This is the task of the owners. Situations with hacking of cryptocurrency exchanges or other services for storing private keys cannot be compared with the weak protection of a Bitcoin wallet or blockchain system.
What are the ways
Для взлома электронного кошелька применяются следующие способы:
- obtaining user data and logging into an account;
- intelligent attack by downloading the Qiwi hack app.
Fraudsters use a lot of ingenuity to gain access to the wallet profile and take advantage of other people’s funds. Users are afraid for their money, but they themselves make a lot of mistakes and get into unpleasant situations.
Hacking without additional programs
Hacking a Qiwi wallet is most often carried out through cunning machinations by intruders.
Для получения кода из СМС или пароля для личного кабинета они могут:
- send messages to mail or a mobile device under the guise of a support service;
- make voice calls on behalf of a security officer and request personal ones for verification.
One of the frequent ways is inattention when visiting the terminal. In this case, the user enters his own profile on his own, performs the necessary operations and leaves, forgetting to log out of the account. The system automatically goes to the main menu after a few minutes and exits the profile, but scammers can take advantage of this and withdraw all the money to a personal account.
Another option for fraud without installing applications is the offer to double the funds.
The scam works like this:
- a Qiwi client stumbles upon an ad on the internet detailing how to double their account;
- sends money to the specified details and waits for the receipt of the increased amount.
The user will not receive his money either in a minute or in a year. This is a standard scam that does not require wallet hacking and is based on the Qiwi client’s thirst for easy money. The user independently sends money to the specified account, and advertising information from the site disappears after a few hours. In this case, it is no longer possible to return the money.
Qiwi Hack
A program for hacking Qiwi is widespread on the network, for the activation of which you need to pay money. The developers offer to receive data from any wallet and quickly withdraw funds to the specified details.
Для поиска приложения:
- Open a browser on the computer.
- In the search bar, enter the query: “download Qiwi Hack Final”.
- Go to one of the pages.
- Download application.
Access to keys when hacking a btc wallet
Bitcoin is a public ledger called Blockchain. It stores information about all network transactions and their associated wallets. Owning bitcoins means that the client only has a private key for access. You can store the keys in any form – on a hard drive or flash drive, print addresses in the form of QR codes, store them in a bitcoin bank, etc.
Attackers are not interested in wallets that store a couple of bitcoins. They need Internet services in databases that store many keys or BTC. These are bitcoin exchanges, miners, online stores and owners of large amounts of bitcoins.
Once a potential victim is identified, attackers attempt to gain access to private keys or databases. To do this, all methods of hacking computer systems are used – hidden downloading of viruses on a computer or server of a bitcoin client. Methods for obtaining passwords directly from the client (social engineering methods) are also used. If access to the keys is obtained, then nothing prevents you from transferring bitcoin to the necessary wallets.
The future of technology
He also suggested that those who use the brainwallet consider an improved implementation of this idea – WarpWallet.
Castelucci says the WarpWallets equation has an integrated “salt”—random data used as input when the function hashed. This means that if the user’s “salt” was his email address, the potential thief needs to know not only the password, but also the address.
However, Castellucci advises those who use brainwallet wallets to use sets of random numbers and symbols. Better yet, use diceware, a process by which passwords are generated using a pair of random number generators.
It’s really, really hard to keep people from choosing a dog’s name and their birthday as a password. No script can save people who use «P@ssw0rd». Many users thought that a long phrase as a password is quite safe. However, I have shown that this is not always true.
Castelucci didn’t say exactly how many keyphrases Brainflayer can guess on a single computer. But he hints that if his program is launched in a botnet, then the figure could approach one hundred billion keyphrases per second. Moreover, he says PassPhrase is optimized for the task of quickly generating Bitcoin keys and scanning the blockchain.
To scan and validate the blockchain in the most efficient way, he used a technique known as the Bloom filter. Its result does not yet reach the trillion key phrases per second, which Snowden had previously warned about, implying the achievements of the NSA. However, this may come as a surprise to many people who think their keywords are safe.
What led to the explosive growth of cryptocurrencies
The explosive nature of the growth of cryptocurrencies confirms the high interest in new digital assets. The aggressive appreciation of coins is due to the desire to get away from the outdated banking system, which is trying to take a percentage of each transaction.
In addition to the growth of the rate of individual coins, the market itself is growing. Anyone can raise investments to implement their idea through an ICO. This is how the well-known cryptocurrency Monero (XMR) appeared, the founders of which focused on anonymity, as well as reducing the complexity of mining. There are projects implemented at the state level. This increases people’s interest in blockchain projects created with noble goals, which encourages people to buy cryptocurrency.
The beginning of the era of cybercrime – when bitcoin wallets began to be hacked
It all started in the middle of 2013, when the first bitcoin users started experiencing brainwallet security issues. Around the same time, a Reddit user known as btcrobinhood (BTC Robin Hood) started stealing coins from brainwallets. Then they returned to their rightful owners. So he wanted to show the vulnerability of technology.
Inspired by this example, Castellucci created the original Brainflayer cracker, which could generate 10,000 passwords by predicting every possible guess. When he returned to his computer running the program, he found 250 BTC already taken from someone else’s wallet. Castellucci was placed in a difficult situation. He had two options: take a few BTC as payment for his research, or warn wallet users that their security was at stake. As a result, he managed to contact the “victim”. He was able to convince him to move the bitcoins to a secure wallet.
For a time he worked on his research. He hoped the problem would go away. After all, many experts said that the brainwallet has many vulnerabilities. When the problem persisted, he decided to return to research, claiming that it was his responsibility to reveal weaknesses so that users could take appropriate action and increase their level of security.
Adylkuzz Hidden Miner Hacks Bitcoin Wallets
We all remember the WannaCry ransomware virus that infected half the planet. But there are more cunning hackers who, even before this ransomware, quietly made money using a hole in the Windows operating system. The virus does not require anything from the user, does not steal funds, but at the same time actively penetrates financial institutions.

We are talking about the Adylkuzz miner. It infected hundreds of thousands of servers and computers of ordinary users. Even companies operating in the public sector, the banking sector, the fuel and energy complex, and the transport industry suffered from it. The purpose of the malware is to take over your computer and mine cryptocurrency at your expense.
There have been attempts to hack into corporate networks before. Hackers mined bitcoins at the expense of the computing power of the company’s servers. In addition to bitcoins, the attackers mined lightcoins and other coins that were profitable to mine at that time. This software exploits the same Windows vulnerability as the WannaCry bitcoin ransomware.
Inside the hidden miner, Eternalblue and Doublepulsar files were found. These tools were stolen by hackers from The Shadow Brokers from the Equation Group, which is associated with the American NSA. Throughout 2016-17, experts argued that the virus would be profitable. This turned out to be true.
In addition to corporate networks, hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of PC users have been infected by accidentally installing malware on their computers. The infection occurred through torrents, suspicious sites, services. The highest percentage of viruses was recorded in archived files.
Of course, the virus does not encrypt anything and does not extort money. But if the server is loaded, the presence of a hidden miner leads to overload and critical problems. On infected servers, system administrators often observed the “blue screen of death”, as well as the instability of the corporate network.
During mining, Adylkuzz steals a significant portion of server performance. Each infected computer scans and tries to break into machines that are part of the same network. Internet sites that generate huge amounts of traffic are also infected. This leads to network resource overload. What causes component servers.
QIWI scam
The desire to hack a Qiwi wallet can serve as a good lesson for someone who is trying to find a way to do it.
People have always wanted to make money, usually on a large scale and in a very short period of time without doing much of anything. A lot of advertisements in the form of “Magic Wallets” have long appeared on the Internet. The essence of which is very simple. You send money to the account of this wallet, after some time the amount is returned to the account several times more than the amount sent. All this information is presented in such a way that the user, while trying to hack the Qiwi wallet, accidentally stumbled upon this information. Below, as usual, in the form of a comment along the lines of “I succeeded, it’s unbelievable but true.” But this is all deception. First, you send 100 rubles for verification – and return 200. Sending 100 again – a return of 200. When you are already convinced that all this works, you do not hesitate to send the maximum amount that you have on your account. But this time, alas, the money does not increase and does not come back. That’s how the system is designed.
Some people, having fallen for such a trick, get angry, write something in the form – “I got caught on this and now I want to take revenge.” You are offered to send a small amount of not more than 800 rubles, then the system will return you constantly. Of course, the QIWI number, on which they allegedly got caught, substitute their own. And as anyone understands, this is also a hoax. You won’t get a dime if you send funds to their account.
Social engineering and phishing
Social engineering refers to a set of exchange techniques that force users to perform actions on websites or applications that can harm them. One of these very popular methods is phishing – the creation of clone sites of well-known resources that force users to disclose their personal data, including passwords, phone numbers, bank card details, and, in recent years, private keys to cryptocurrency wallets.
Links to phishing sites can be distributed in many ways: social media advertisements, emails. All this is done with the sole purpose of forcing an inattentive user to go to a fake site so that he enters personal data there.
According to Chainalysis, phishing remained the most profitable scam in the cryptocurrency space throughout 2017-2018. However, if in 2021 it accounted for more than 88% of all fraudulent schemes, then in 2021 this method has become less effective, and its success rate has already dropped to 38.7%.
The danger of becoming a victim of a phishing attack still exists. Among the latest such incidents are the attacks on the popular Electrum wallet in December 2021 and April 2021. Often, attacks were also carried out on altcoin wallets.
In addition, Bitfinex and Binance exchanges, the Trezor hardware wallet, the LocalBitcoins platform for buying/selling bitcoins, as well as users of social networks such as Facebook have recently become victims of phishing attacks. In the latter case, the attackers copy the pages of popular cryptocurrency communities, after which they use photos of members of real communities, marking them in the post as winners of the platform loyalty program.
The fact that Binance Labs, the venture arm of the Binance cryptocurrency exchange, has invested in PhishFort speaks volumes about the importance that industry leaders attach to the fight against phishing. The company specializes in protection against phishing attacks. It focuses on businesses that are in a high risk group: bitcoin exchanges, ICO projects, token issuance platforms.
The recommendations for protecting against phishing attacks are quite simple: improving general computer literacy, personal attentiveness (manually entering URLs and checking the use of the https protocol), as well as distrusting ads offering free distribution of cryptocurrencies.
Mobile applications
Most often, the victims of hackers are owners of Android devices, instead of 2FA using only a login and password. This happens, among other things, because the process of adding applications to the Google Play Store is less strict than that of the App Store. Attackers take advantage of this by hosting their own applications that imitate well-known wallets and exchanges and lure sensitive data from inattentive users.
One of the high-profile stories with fake applications was related to the stock exchange Poloniex. In November 2021, ESET experts discovered a program on Google Play that pretended to be the official mobile application of this American exchange. The essence of the fraud was that the users who downloaded the program entered their login and password there. This allowed the creators of the virus to independently change settings, perform transactions, and also gain access to users’ mail.
Despite the fact that at that time Poloniex did not have official mobile applications (they were released only in July 2018), two variants of fake applications were installed by more than 5 thousand people. After a warning from ESET, they were removed from Google Play.
Also on Google Play were fake apps MetaMaskand Trezor Mobile Wallet.
Users of iOS devices are more likely to become victims of cybercriminals who distribute applications with a built-in hidden mining function. After the discovery of this issue, Apple was forced to tighten the rules for accepting applications in the App Store. At the same time, the damage from such applications is quite small – they only reduce the performance of the computer without stealing money.
Recommendations: do not install applications that are not absolutely necessary. Do not forget about two-factor authentication, and also check the links to applications on the official websites of the projects and the platform to make sure they are authentic.
Trojan viruses to hack btc wallets
Это разновидность вредоносных программ, проникающих в компьютер под видом легального ПО. Они осуществляют различные неподтвержденные пользователем действия:
- collection of information about bank cards,
- computer malfunction,
- use of computer resources for mining purposes,
- using IP for illegal trade, etc.
But the ingenuity of hackers does not stand still. Thus, a new version of the infamous Trojan was discovered Win32.Rakhni. This virus is still known с 2013 года, but if at first it focused solely on encrypting devices and demanding a ransom for unlocking, then the new version went much further.
First, it checks for folders associated with bitcoin wallets and, if found, encrypts the computer and demands a ransom. However, if no such folders are found, Win32.Rakhni installs a malware that steals computer processing power for the purpose of covert mining of cryptocurrencies, and also tries to spread to other devices on the network.
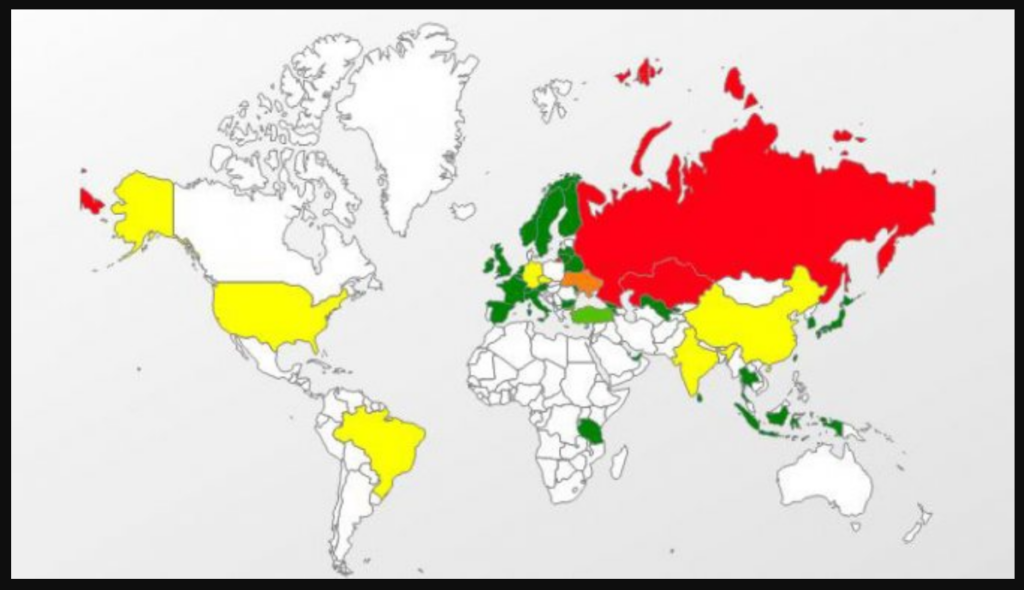
At the same time, as can be seen in the image above, more than 95% of all cases of infection of computers with this Trojan accounted for Russia, the second and third places went to Kazakhstan and Ukraine.
According to the data Kaspersky Labs, Win32.Rakhni, it is most often distributed through emails, in which users are prompted to open the attached pdffile, but instead of the expected content, a malware program is launched.
As with phishing attacks, basic computer hygiene and the utmost care when opening attachments are essential to prevent infection of devices.
Types of bonuses in Qiwi
So, you are interested in free money. In 2022, there are a sufficient number of resources that distribute certain amounts for certain actions to Qiwi users.
Есть три вида:
- Registration fee.
- Platforms issuing vouchers that are missing characters. You can get a reward if you guess them.
- Sites that give gifts for entering an electronic wallet.
Free money is also distributed by casinos, bookmakers and similar services. However, these are risky options that we will not consider.
Keyloggers (keyloggers)
Malicious programs often consist of several components, each of which performs its own task. One of the popular attack methods is the so-called keyloggers (keyloggers). This is a highly specialized tool that records all keystrokes on devices. With its help, attackers can quietly take over all the user’s confidential information, including passwords and keys from cryptocurrency wallets.
Most often, keyloggers penetrate systems as part of complex malicious software, but sometimes they can be embedded in completely legal software.
As a rule, antivirus software manufacturers add well-known keyloggers to their databases, and the method of protection against them is not much different from the method of protection against any other malicious software. The problem is that there are a lot of keyloggers. Keeping track of everyone is physically very difficult. For this reason, keyloggers are often not detected by antiviruses on the first try.
Watch out for security
In our articles and videos on the YouTube channel, we have repeatedly written and said that it is very dangerous to store on exchanges!
Therefore, we advise you to think about the future and protect yourself.
Это можно сделать 2 способами:
- Buy a reliable hardware wallet Ledger Nano S or Ledger Nano X
- Install under all your cryptocurrencies.
Public WiFi networks
Theft of funds over public Wi-Fi networks has always been and remains one of the most popular tools for attackers. Most Wi-Fi routers use the WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) protocol, which not only encrypts all information on the wireless network, but also ensures that only authorized users can access it.
However, the hackers found a loophole. By running a simple KRACK command, they force the victim’s device to reconnect to its own Wi-Fi network. After that, they get the opportunity to track and control all the information passing through it, including the keys to cryptocurrency wallets.
Regular router firmware updates help protect against such an attack, as well as your own care: you should never make transactions while in public places, such as train stations, airports, hotels, or, which happens quite often among representatives of the bitcoin community, at blockchain conferences.
Distribution of malware
Some users, in order to save money, purchase unlicensed software, which can cost several times cheaper, or be distributed free of charge. Sometimes it is even suggested to download a program for hacking a Qiwi wallet.

The Qiwi system has an option of SMS informing, which costs 29 rubles per month. Some users turn off SMS notifications in order to save money or not want to enter a code every time they log in. This is what the scam is based on:
- Through the installation of malicious software, fraudsters receive keys to enter the QIWI wallet.
- If SMS notification is disabled on the account, third parties will be able to enter the QIWI personal account and perform any operation with the user’s account.
Before the owner of the wallet enters the site and discovers the loss, his funds will already be withdrawn from the system. In this case, the security service will not be able to help. For your own safety, you should not download unlicensed programs or perform any actions on suspicious resources. Also, do not turn off SMS informing, as this can lead to significant financial losses.
It should be noted that QIWI never offers to install this or that program. If you need to install the Qiwi application, then only official stores can be used for this purpose.
Slack bots
There are also Slack bots. They send a notification to the user about a problem with the wallet. The end goal is to get the person to click on the message and enter the private key.
The largest successful hack involving Slack bots was the Enigma incident in August 2017. Then the project was forced to suspend the pre-sale of ECAT tokens after unknown attackers hacked the project’s website and, using a false ETH address, deprived it of more than $400,000.
Extensions, plugins and addons for browsers to hack btc wallets
There are many browser extensions and plugins. They help make interaction with cryptocurrency wallets easier and more comfortable. However, they are usually written in JavaScript, which makes them vulnerable to hacker attacks. We can talk about intercepting user data and further access to wallets, as well as installing programs for hidden mining.
At the same time, as Check Point Software Technologies Ltd noted, it is hidden cryptominers that remain the dominant threat to organizations around the world.
There are several ways to counter this threat: install a separate browser or even a separate trading computer, use incognito mode, regularly update anti-virus databases and do not download any dubious extensions or plug-ins.
The main part of hacker attacks falls on exchanges and companies. However, they also do not ignore individual users. Hackers are one step ahead of the industry. An important aspect of the fight against intruders remains their own computer literacy of users and tracking the latest trends and developments in the field of cybersecurity.
Over the years, the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry has developed a reputation as a frequent victim of cyberattacks . It is generally accepted that cryptocurrency exchanges and exchangers are becoming the most common target for attacks, constantly exposing their clients’ funds to excessive risk and regularly losing hundreds of millions of dollars. But how well deserved is this reputation?
It is difficult to argue that this was indeed the case in the early years of cryptocurrencies . The case of the Mt. Gox , one of the first and largest cryptocurrency thefts, is still an example of gross negligence and incompetence that led to the loss of $400 million in bitcoin .
However, today we will look at the history of the biggest crypto heists of all time and see for ourselves that the situation is improving. Government involvement and industry self-regulation initiatives have greatly enhanced security across all major crypto exchanges .
However, this does not mean that crypto investors should start or continue to keep their funds on crypto exchanges. No matter how secure any particular platform will be, it is almost by definition more vulnerable to attack than more secure storage methods : primarily cold wallets .
Even if hackers manage to break through all the defenses, closer collaboration among the major players in the crypto space, advances in blockchain forensics, and asset insurance coverage often result in the swift recovery of stolen funds or, failing that, full compensation for losses. So, let’s take a look at how the biggest crypto heists in history happened and what they led to.
Hack Poly Network
Attack Date: August 10, 2021
Стоимость потерянных активов: 610 миллионов долларов.

The Poly Network hack, a cross-chain interoperability protocol for Bitcoin ( BTC ), Ethereum ( ETH ), Neo ( NEO ) and other cryptocurrencies, is the largest confirmed cryptocurrency heist in history , and also one of the most recent. Poly Network’s cross-chain transaction feature allows users to transfer assets between different blockchains without having to convert them through exchanges.
According to programmer Kelvin Fichter , the protocol creates digital self-managed safes on two different blockchains . It then allows the user to withdraw funds from one box only after they receive confirmation from the other box that the corresponding amount of assets has been deposited into it.
The hacker (or hackers) managed to find a way to trick the safe box into releasing the funds stored in it without obtaining legal permission from another blockchain. They exploited this vulnerability on August 10 to steal over $610 million in total .
Fortunately, this story has a happy ending. The Poly Network team made contact with the hacker shortly after the attack, which eventually led to the return of all $610 million worth of stolen assets.
Coincheck hack
Attack date: January 26, 2018
Стоимость потерянных активов: 534 миллиона долларов

Coincheck is a fairly popular Japanese cryptocurrency exchange that was attacked by unknown hackers in January 2018. About 523 million NEM (XEM ) tokens , valued at that time at $530 million , were illegally withdrawn from the exchange’s address on January 26 , after which there was an abnormal decrease in the exchange’s balance.
By Coincheck’s own admission , the attack was made possible due to technical difficulties and a lack of staff that the company faced , which eventually led to security breaches. The stolen NEM was stored in an internet-connected hot wallet , rather than an offline cold wallet, which is standard industry practice as it provides an additional layer of protection against online attacks .
The Japan Financial Services Agency (FSA) subsequently ordered Coincheck to improve its security practices. However, the exchange was not closed, in the hope that it would be able to return the money to users and restore to normal operation. The FSA’s decision to let the exchange continue to operate proved to be the right one, as Coincheck used its own capital to refund all 260,000 affected customers and remains a highly active trading platform with nearly $100 million in daily trading volume as of August 2021 .
The tragedy of Mt. gox
Date of attack: late 2011 – February 2014
Стоимость потерянных активов: 460 миллионов долларов

Mt. Gox was created in 2007 by American programmer Jed McCaleb to serve as a card exchange platform for the popular game Magic: The Gathering Online. McCaleb never fully implemented the original plan, reclassifying the site as a bitcoin exchange in 2010 . Later, when the company’s popularity and the volume of funds flowing through it began to skyrocket, he sold it to the Japanese programmer and French-born entrepreneur Mark Karpeles (Mark Karpeles) .
Karpeles’ subsequent actions were disastrous for business. While the trading platform has grown to become the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the world , processing up to 70% of all BTC transactions at once , the development of its internal mechanisms has stalled. This made her an ideal target for hackers.
In an interview with Wired, anonymous Mt. Gox reported that the exchange’s software development cycle lacked even basic things like version control and a test environment , which caused updates to be released too slowly and vulnerabilities remained unpatched for several weeks. Hackers took advantage of existing security holes and were able to steal 744,408 bitcoins from the exchange, worth about $ 460 million at the time of the theft, or $37 billion at today’s exchange rate . This has been going on for several years since the end of 2011 .
Mt. Gox finally collapsed on February 24, 2014, filing for bankruptcy soon after. The lost funds have not been fully reimbursed to the exchange customers, however, many of them still do not give up hope. Robbery Mt. Gox became the biggest crypto theft for years until Coincheck surpassed it four years later. It also served as a lesson, showing the world that the crypto industry has become too big to neglect professional security measures to protect client money.
KuCoin hack
Date of attack: September 25, 2020
Стоимость потерянных активов: 280 миллионов долларов

Next on our list is KuCoin , another major crypto exchange that was hacked on September 25, 2020, stripping $275-$285 million of user assets . In this case, it can be noted that the quick and accurate actions on the part of the exchange, coupled with close cooperation with other companies in the cryptocurrency industry, allowed KuCoin to survive after the incident.
Within a week of the hack, blockchain data processing company Chainalysis traced all the stolen funds and was able to get on the trail of the criminals. Their Reactor crypto-forensic tool kept the money out of sight, despite the attempts of criminals to disguise the movement of funds through coin mixers and decentralized exchanges ( DEXs ) , which usually leave no trace.
Through the use of blockchain tools and cooperation with other exchanges and law enforcement agencies, KuCoin recovered 84% of the stolen tokens , and covered the remaining losses with its own capital and insurance fund . Moreover, after the attack, the exchange established the Safeguard Program to enable other crypto companies to benefit from their invaluable experience in dealing with the consequences of a hack, if they find themselves in a similar situation.
With its skillful approach to resolving the incident, KuCoin earned the respect of customers and rightfully ranked sixth among the leading cryptocurrency exchanges with a daily trading volume of about $1.92 billion as of August 2021 .
CryptoCore/Lazarus hack
Date of attack: January 2018 – to date
Стоимость потерянных активов: от 200 млн до 1,75 млрд долларов

The history of the CryptoCore hacker group is a bit like that of Mt. Gox in the sense that the attack was not a single event, but happened gradually, over several years. However, the difference is that at least five different exchanges were targeted by the attack .
A study published by cybersecurity experts ClearSky in June 2020 found that as early as May 2018, a group of hackers had compromised a number of crypto exchanges through elaborate phishing attacks, resulting in the loss of at least $200 million in crypto . ClearSky named the group “CryptoCore”, identifying with medium confidence that it was based in Russia, Ukraine, or Romania, and found that the affected exchanges were primarily based in Japan and the United States .
But here’s where it gets interesting: Further investigation by ClearSky uncovered links to another hacker group. In May 2021, the company released a report that attributed the medium-to-high probability CryptoCore attacks to the Lazarus hacking team . They are believed to be based in North Korea and work for the government of the country, in connection with which they are also included in the list of active threats to US national security .
If ClearSky’s assessment is correct, these CryptoCore/Lazarus hacks combined are one of the largest cryptocurrency thefts of all time . Another study by the already mentioned firm Chainalysis in February 2021 found that Lazarus had stolen as much as $1.75 billion in cryptocurrencies . The attacks began around January 2018 and are likely to continue to this day – the group has yet to be finally identified or apprehended.
Bitgrail hack
Date of attack: February 10, 2018
Стоимость потерянных активов: 140-195 миллионов долларов

Bitgrail was the complete opposite of the successful cases of KuCoin and Bitfinex (more on that later). The exchange was attacked in January-February 2018, resulting in the theft of 17 million Nano (NANO) tokens worth about $ 140-195 million .
The fact is that the founder and sole director of the company, Francesco Firano, made mistake after mistake. Even though the hackers started siphoning off Nano in January, the exchange did not shut down and notify the authorities until Feb. 10 , when it was already too late. After that, Firano unsuccessfully tried to shift the blame to the Nano team, which rightly refused to change the blockchain in any way in order to compensate for the Bitgrail security error .
Worse, as the investigation into the break-in continued, Italian police found evidence of Firano’s “clear” personal involvement in the attack . Although the authorities were not sure whether he was actively involved in the theft or simply committed malpractice, they charged Firano with computer fraud, fictitious bankruptcy and money laundering.
As of August 2021, the situation remains unresolved, with an Italian court ordering Bitgrail to refund as much of the stolen funds as possible, and victims’ claims remain pending until September 17, 2021, as stated on the exchange’s website.
Bitfinex hack
Date of attack: August 2, 2016
Стоимость потерянных активов: 78 миллионов долларов

Bitfinex is another crypto exchange that lost a large amount of client funds as a result of a hack, but eventually recovered in a remarkable way. The exchange was attacked on August 2, 2016 , and almost 120,000 bitcoins were withdrawn from users’ wallets , which was equivalent to $78 million at that time.
The exchange announced the hack on its blog and immediately stopped BTC withdrawals and all trading. All the stolen funds were soon blacklisted (preventing the possibility of cashing them out through any cryptocurrency exchange), but were never returned, and the hackers themselves were never tracked down, despite their best efforts.
To compensate the victims of the attack, Bitfinex issued BFX tokens, issuing them to the victims at a ratio of 1:1 to their losses , promising to buy back the tokens at 100% of their value using future profits. The exchange successfully met its obligations within a year of the attack by announcing a full buyout of BFX in April 2017 .
The graceful resolution of a seemingly catastrophic situation has allowed Bitfinex to remain among the most popular crypto exchanges in the world. As of August 2021, it is the eighth largest platform with a daily trading volume of around $900 million.
Africrypt hack
Attack Date: April 13, 2021
Стоимость потерянных активов: от 100 млн до 3,6 млрд долларов

Last but not least on our list is the mysterious Africrypt case. The South African investment firm, founded in 2019 by brothers Raees and Ameer Cajee, ceased all operations on April 13, 2021 , citing a security breach of the system, client accounts, client wallets and nodes .
The brothers then advised their clients not to follow the “legitimate path” of recovering funds lost in the attack, as this would only delay the process of tracking and returning them. Not heeding Keiji’s advice, several victims of the incident approached the law firm Hanekom Attorneys . They filed a police complaint claiming the amount of losses was $3.6 billion in bitcoin and suggesting that the alleged hack was an exit scam, aka runaway with clients’ money .
In response, Reis and Amir hired their own lawyer, John Oosthuizen, who strongly denied the involvement of the brothers in the robbery. Oosthuizen added to the absurdity of the situation, explaining the fact that the Cages did not contact the police immediately after the break-in was due to their young age and lack of life experience. (The brothers were 18 and 20 years old at that time, and, most likely, they knew about the existence and goals of law enforcement.).
As you might guess, the Africrypt website was shut down and its founders mysteriously disappeared shortly after the incident. So far, it is only unclear whether the estimated loss of $3.6 billion is correct. To date, there is no evidence that the company has ever disposed of such a volume of funds, but if it is confirmed, it will put Africrypt in the first place among the largest cryptocurrency thefts in history.

Telegram: https://t.me/cryptodeeptech
Video: https://youtu.be/LvIfQM9VU4U
Source: https://cryptodeeptech.ru/history
