Parity Technologies, the company behind blockchain protocol Polkadot, has released Substrate 2.0. This new technology aims to make building custom blockchains easier.
In a blog post published on Sept. 23, Parity communications manager Phil Lucsok explained the bells and whistles of Substrate 2.0. The post claims that these new tools give developers easy access to all the functionality of a Web 3.0 blockchain.
The aim of Substrate 2.0 is to help developers build their own blockchains, with Polkadot and Kusama already running Substrate 2.0. Polkadot took the blockchain world by surprise when it surged into the crypto Top 10.
Co-founder of Parity Gavin Wood believes that these different blockchains will be able to communicate with one another. For example, Kusama, which acts as a sort of live testnet for Polkadot, is set to be able to seamlessly exchange information with Polkadot, even though they are different blockchains.
With the advent of these new tools, specific aspects of each blockchain could communicate as well. For example, users could exchange identities but not wallet balances across chains.
New Toys
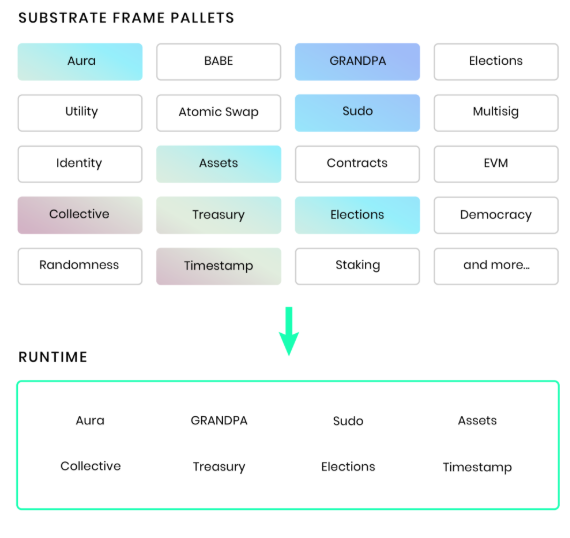
As part of a way to attract developers to the Parity platform, the tech company has introduced modules they call “pallets.” Pallets for all different kinds of popular functionalities exist on Substrate 2.0.
For example, there is a pallet that mimics the Ethereum Virtual Machine, one that allows for governance voting, and yet another that integrates proof-of-stake (PoS).
These pallets can be integrated or removed easily from blockchains built on Parity. The idea is to give developers more freedom and save time. All told, there are about 70 pallets.
On-Off Chain and IoT

Leveraging all sorts of blockchain capabilities, Substrate 2.0 also makes use of what it calls “off-chain workers.” This function is optimal, Parity says, for using an Internet of Things (IoT) model. It allows off-chain data to come onto the blockchain without having to integrate all the information into nodes.
The blog post gives the example of a PoS holder being able to tell the blockchain that it is active to be a validator. This theoretically should remove a large burden of processing power, Parity says.
While Ethereum works towards Ethereum 2.0, the blockchain scalability problem has yet to find a popular solution. Other approaches to blockchain are getting a chance to shine in the DeFi-fueled renewed interest in crypto.